Comprehensive Guide to COPD Drugs for Effective Symptom Management
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease affects millions worldwide, making breathing increasingly difficult over time. While there is no cure for COPD, various medications can significantly improve quality of life by managing symptoms, reducing inflammation, and slowing disease progression. Understanding the different types of drugs available and how they work helps patients and caregivers make informed decisions about treatment options.
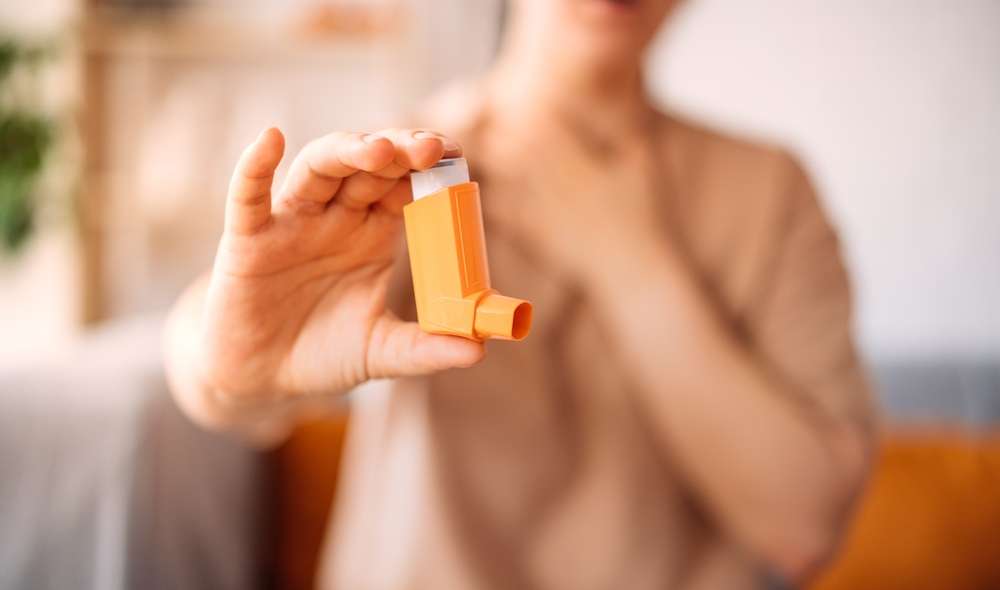

Managing COPD requires a comprehensive approach that combines lifestyle changes, medical supervision, and appropriate medication. The right combination of drugs can help patients breathe easier, reduce exacerbations, and maintain independence longer. Healthcare providers typically prescribe medications based on disease severity, symptoms, and individual patient needs.
Understanding COPD and the Role of Medications
COPD encompasses two main conditions: chronic bronchitis and emphysema. These conditions cause airway inflammation, mucus buildup, and damaged air sacs in the lungs. Medications work by targeting different aspects of the disease process. Bronchodilators help open airways, anti-inflammatory drugs reduce swelling, and mucolytics thin mucus for easier clearance. The goal is not to cure COPD but to manage symptoms effectively and prevent complications.
Medications are typically delivered through inhalers, nebulizers, or oral tablets. Proper technique when using inhalers is crucial for medication effectiveness. Many patients benefit from combination therapies that address multiple symptoms simultaneously.
5 Types of Medications for COPD Treatment
Short-acting bronchodilators provide quick relief during breathing emergencies. These rescue medications, including albuterol and ipratropium, work within minutes but last only 4-6 hours. Long-acting bronchodilators offer sustained relief for 12-24 hours and include medications like tiotropium and formoterol.
Inhaled corticosteroids reduce airway inflammation and are often combined with bronchodilators. Common examples include fluticasone and budesonide. Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors like roflumilast help reduce inflammation and are typically prescribed for severe COPD with frequent exacerbations.
Mucolytics such as guaifenesin help thin mucus, making it easier to cough up and clear from the airways. These medications are particularly helpful for patients with chronic bronchitis who produce excessive mucus.
| Medication Type | Common Examples | Monthly Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Short-acting bronchodilators | Albuterol, Ipratropium | $30-80 |
| Long-acting bronchodilators | Tiotropium, Formoterol | $200-400 |
| Inhaled corticosteroids | Fluticasone, Budesonide | $150-350 |
| Combination inhalers | Advair, Symbicort | $300-500 |
| Mucolytics | Guaifenesin, Acetylcysteine | $20-60 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Natural Remedies and Supportive Treatments
While medications form the cornerstone of COPD treatment, natural remedies and supportive treatments can complement medical therapy. Breathing exercises, particularly pursed-lip breathing and diaphragmatic breathing, help improve lung function and reduce shortness of breath. Pulmonary rehabilitation programs combine exercise training, education, and support to help patients manage their condition better.
Nutritional support is essential since COPD patients often experience weight loss and muscle weakness. A diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and adequate protein can support lung health. Staying hydrated helps thin mucus secretions naturally.
Oxygen therapy may be prescribed for patients with severe COPD who have low blood oxygen levels. Portable oxygen concentrators allow patients to maintain mobility while receiving supplemental oxygen. Some patients also benefit from non-invasive ventilation devices during sleep.
Managing Side Effects and Drug Interactions
COPD medications can cause side effects that vary depending on the specific drug and delivery method. Inhaled bronchodilators may cause tremors, rapid heartbeat, or nervousness. Corticosteroids can increase infection risk and may affect blood sugar levels in diabetic patients.
Patients should inform their healthcare providers about all medications, supplements, and health conditions to avoid dangerous interactions. Regular monitoring helps ensure medications remain effective and safe over time.
Creating an Effective Treatment Plan
Successful COPD management requires ongoing collaboration between patients and healthcare teams. Treatment plans should be individualized based on symptom severity, lifestyle factors, and treatment goals. Regular follow-up appointments allow for medication adjustments as the disease progresses.
Patients should learn proper inhaler techniques, understand when to use rescue medications, and recognize signs of exacerbations that require immediate medical attention. Having an action plan helps patients respond appropriately to symptom changes.
Effective COPD drug therapy can significantly improve breathing, reduce hospitalizations, and enhance overall quality of life. Working closely with healthcare providers ensures patients receive the most appropriate medications for their specific needs while minimizing side effects and complications.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.