How to Recognize Breast Cancer Signs in 2025: Early Detection, Risks, and Resources
Breast cancer continues to be one of the most prevalent cancers globally, affecting millions of individuals each year. While significant progress has been made in research and treatment, early detection remains crucial for improving survival rates and outcomes. Recognizing the warning signs and promptly seeking medical attention can mean the difference between early, treatable detection and more advanced disease. This article provides an in-depth overview of the most important signs to watch for, outlines risk factors and diagnostic methods, and offers guidance on accessing further resources. The information is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. If you have concerns about your health, consult a qualified healthcare provider.

What Is Breast Cancer?
Breast cancer is a disease characterized by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the breast tissue. It can occur in both women and men, although it is far more common in women. Breast cancer typically begins in the cells of the lobules (milk-producing glands) or the ducts (passages that carry milk to the nipple). In rarer cases, it can start in other breast tissues.
The development of breast cancer is influenced by various factors, including genetics, hormones, and environmental elements. While some risk factors, such as age and family history, cannot be changed, others, like maintaining a healthy lifestyle, can be modified to potentially reduce the risk of developing breast cancer.
Types of Breast Cancer – Common & Rare Forms
Breast cancer is not a single disease but rather a group of diseases with different characteristics and behaviors. Understanding the various types of breast cancer is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment planning.
Common forms of breast cancer include:
-
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS): A non-invasive breast cancer confined to the milk ducts.
-
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC): The most common type, starting in the milk ducts and spreading to surrounding breast tissue.
-
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (ILC): Begins in the milk-producing lobules and can spread to other parts of the breast.
Rarer forms of breast cancer include:
-
Inflammatory Breast Cancer: A fast-growing cancer that causes the breast to appear red, swollen, and warm.
-
Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A type that lacks the three most common receptors known to fuel breast cancer growth.
-
Paget’s Disease of the Nipple: A rare form that begins in the nipple and often extends to the areola.
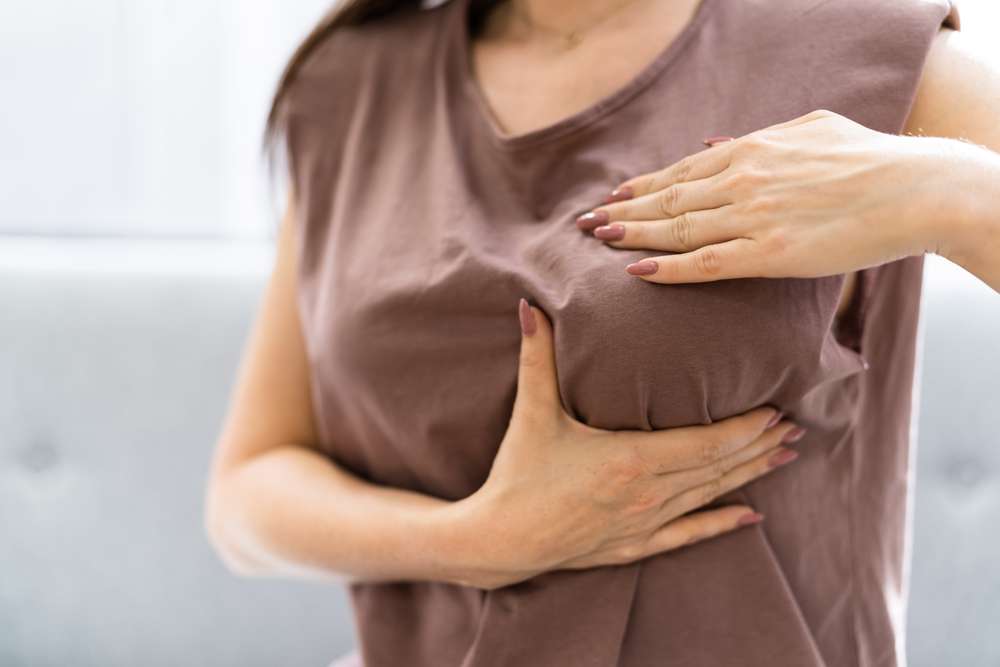
Red Flag Warning Signs
Recognizing the warning signs of breast cancer is crucial for early detection. While regular screenings are important, being aware of changes in your breasts can lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment. Key warning signs to watch for include:
-
A new lump or mass in the breast or underarm area
-
Thickening or swelling of part of the breast
-
Skin irritation or dimpling
-
Redness or flaky skin in the nipple area or the breast
-
Pulling in of the nipple or pain in the nipple area
-
Nipple discharge other than breast milk
-
Any change in the size or shape of the breast
-
Pain in any area of the breast
It’s important to note that these signs do not necessarily indicate breast cancer, but they warrant prompt medical attention for proper evaluation.
Diagnosis and Screening
Early detection through regular screening and prompt diagnosis of breast cancer can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Current screening and diagnostic methods include:
-
Mammography: X-ray imaging of the breast, recommended annually for women over 40 or earlier for those at higher risk.
-
Clinical Breast Exam: A physical examination performed by a healthcare provider.
-
Breast Self-Exam: Regular self-checks to familiarize oneself with the normal look and feel of their breasts.
-
Breast MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging, often used in conjunction with mammograms for high-risk individuals.
-
Ultrasound: Sound waves used to produce images of breast tissue, particularly useful for dense breast tissue.
-
Biopsy: The removal of a small sample of breast tissue for laboratory analysis, used to confirm a diagnosis.
As technology advances, new screening and diagnostic tools may become available, potentially improving the accuracy and accessibility of breast cancer detection.
Resources for Breast Cancer Information and Support
Numerous resources are available for individuals seeking information about breast cancer, support during treatment, or ways to get involved in breast cancer awareness and research efforts. Some valuable resources include:
-
National Cancer Institute (NCI): Offers comprehensive information on breast cancer, clinical trials, and treatment options.
-
American Cancer Society: Provides education, support services, and resources for patients and caregivers.
-
Breast Cancer Research Foundation: Funds innovative research and raises awareness about breast cancer.
-
Susan G. Komen: Offers education, support services, and funding for breast cancer research.
-
Living Beyond Breast Cancer: Provides programs and services to help people whose lives have been impacted by breast cancer.
These organizations offer a wealth of information, from understanding risk factors and prevention strategies to navigating treatment options and finding support groups.
As we look towards 2025, the landscape of breast cancer detection, diagnosis, and treatment continues to evolve. Staying informed about the latest developments, understanding the warning signs, and utilizing available resources can empower individuals to take an active role in their breast health. Remember, early detection remains one of the most powerful tools in the fight against breast cancer.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.