Organize Your Space: Functional Storage Cabinet Solutions
Clutter can quickly take over a home or office, making it difficult to find what you need and creating unnecessary stress. Storage cabinets offer a practical solution to keep belongings organized, accessible, and protected. Whether you need to store kitchen supplies, office documents, tools, or personal items, the right cabinet can transform chaotic spaces into orderly environments. Understanding the different types of storage cabinets and their features helps you choose options that fit your specific needs and available space.
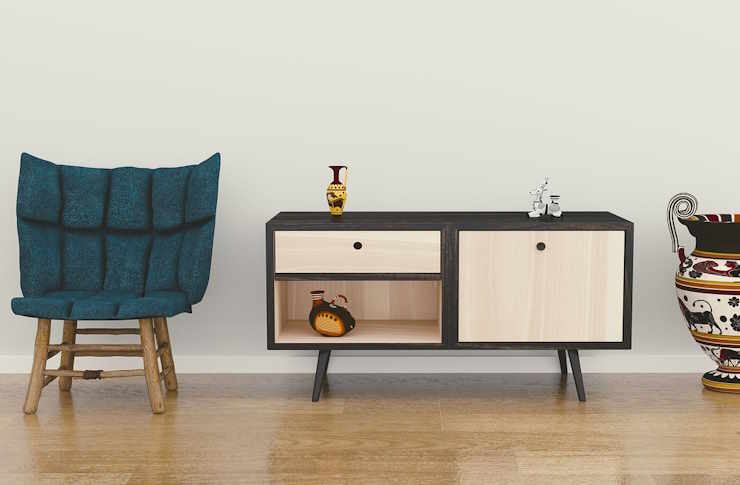

Why Functional Storage Cabinets Matter
Functional storage cabinets serve as essential organizational tools that enhance both residential and commercial spaces. They provide dedicated places for items that might otherwise accumulate on countertops, floors, or desks, reducing visual clutter and improving overall aesthetics. Beyond appearance, well-designed cabinets protect stored items from dust, moisture, and damage while making retrieval easier and faster. In workspaces, proper storage solutions can boost productivity by keeping supplies within reach and maintaining clear work surfaces. In homes, they help maximize limited square footage by utilizing vertical space and underused areas. The right cabinet system creates a sense of order that positively impacts daily routines and mental clarity.
Storage cabinets also contribute to safety by securing potentially hazardous materials away from children or pets. Lockable options provide additional security for valuables, documents, or sensitive items. In professional settings, organized storage demonstrates professionalism and efficiency to clients and visitors. The investment in quality cabinets often pays dividends through improved space utilization, reduced time spent searching for items, and longer-lasting organization systems that adapt to changing needs.
Types of Storage Cabinets
Storage cabinets come in numerous configurations designed for specific purposes and environments. Kitchen cabinets typically feature shelving for dishes, pantry items, and cookware, with options for pull-out drawers and specialized organizers. Garage cabinets are built with durability in mind, often constructed from metal or heavy-duty materials to withstand tools, chemicals, and equipment. Office filing cabinets provide organized document storage with drawer systems that accommodate standard file sizes and locking mechanisms for confidential materials.
Bathroom cabinets range from under-sink vanities to wall-mounted medicine cabinets, designed to handle moisture while storing toiletries and cleaning supplies. Wardrobe cabinets and armoires offer clothing storage with hanging rods, shelves, and sometimes built-in mirrors. Display cabinets feature glass doors or open shelving to showcase collections, books, or decorative items while keeping them dust-free. Modular storage systems allow customization with interchangeable components that can be reconfigured as needs change.
Specialty cabinets address unique requirements such as wine storage with temperature control, media cabinets with cord management for electronics, or hobby cabinets with compartments for craft supplies. Understanding these categories helps narrow choices based on intended use and available space.
Top Organization Tips
Maximizing cabinet functionality requires thoughtful organization strategies beyond simply placing items inside. Start by sorting belongings into categories and discarding or donating items no longer needed. This decluttering step prevents overcrowding and makes it easier to maintain order. Group similar items together and assign specific cabinet sections to each category, creating intuitive storage zones that family members or coworkers can easily remember.
Use adjustable shelving to accommodate items of varying heights and prevent wasted vertical space. Incorporate storage accessories like bins, baskets, drawer dividers, and shelf risers to create smaller compartments within larger cabinet spaces. Clear containers allow quick visual identification of contents without opening multiple boxes. Label shelves, bins, and drawers to maintain organization over time and help others return items to proper locations.
Place frequently used items at eye level or within easy reach, while storing seasonal or rarely needed belongings on higher or lower shelves. Install pull-out shelves or lazy susans in deep cabinets to improve access to items at the back. Utilize door-mounted organizers for additional storage of smaller items. Regularly review and reorganize cabinet contents to adapt to changing needs and prevent gradual disorder from creeping back.
Structural Design Features
The construction and design elements of storage cabinets significantly impact their functionality and longevity. Material selection affects durability, appearance, and cost, with options including solid wood, engineered wood products like plywood or particleboard, metal, and plastic. Solid wood offers superior strength and aesthetics but comes at a higher price point. Metal cabinets provide excellent durability for heavy-duty applications, while plastic options offer lightweight and moisture-resistant solutions for specific environments.
Door styles range from traditional hinged doors to sliding, bi-fold, or roll-up designs, each suited to different space constraints. Soft-close hinges prevent slamming and extend hardware life. Drawer systems with ball-bearing slides operate smoothly and support heavier loads than basic glides. Adjustable leveling feet compensate for uneven floors and protect cabinet bases from moisture damage.
Finish quality protects underlying materials and determines maintenance requirements. Painted finishes allow color customization, while stained wood showcases natural grain patterns. Laminate surfaces resist scratches and moisture, making them practical for high-use areas. Hardware choices including handles, knobs, and locks contribute to both functionality and aesthetic appeal. Ventilation features matter for cabinets storing items that generate heat or require air circulation. Weight capacity ratings indicate how much load shelves and drawers can safely support, an important consideration for heavy items like tools or books.
Choosing the Right Cabinet for Your Space
Selecting appropriate storage cabinets requires assessing available space, storage needs, and budget constraints. Measure the intended installation area carefully, accounting for door clearance, wall obstructions, and adjacent furniture. Consider ceiling height to determine whether tall cabinets or stacked units make sense. Freestanding cabinets offer flexibility and portability, while built-in or wall-mounted options maximize space efficiency in permanent installations.
Evaluate what items need storage and their dimensions to determine required shelf depths, heights, and overall cabinet capacity. Heavier items demand sturdier construction and weight-appropriate shelving. Moisture-prone areas like bathrooms and basements require water-resistant materials and finishes. Security needs may dictate lockable cabinets for valuables or hazardous materials.
Budget considerations extend beyond initial purchase price to include installation costs, hardware upgrades, and long-term durability. While economy options serve temporary or light-duty needs, investing in quality construction often proves more cost-effective over time through extended service life and better functionality. Consider assembly requirements, as ready-to-assemble cabinets reduce upfront costs but require time and skill to construct properly.
Maintaining Your Storage Cabinets
Proper maintenance extends cabinet lifespan and preserves organizational systems. Regular cleaning prevents dust and grime buildup that can damage finishes and hardware. Use appropriate cleaning products for specific materials, avoiding harsh chemicals on wood finishes or abrasive cleaners on painted surfaces. Wipe up spills immediately to prevent staining or moisture damage.
Periodically check and tighten hardware including hinges, drawer slides, and handles that loosen with regular use. Lubricate moving parts with appropriate products to maintain smooth operation. Inspect for signs of damage such as warping, cracking, or water damage, addressing issues promptly before they worsen. Avoid overloading shelves beyond their weight capacity, which can cause sagging or structural failure.
Reorganize contents seasonally to maintain order and remove items no longer needed. This practice prevents gradual accumulation of clutter and keeps storage systems functioning as intended. Address any organizational problems by adjusting shelf heights, adding dividers, or relocating items to more appropriate locations. Well-maintained cabinets continue serving their purpose effectively for many years, protecting your investment and preserving organized spaces.